[ad_1]
Cybersecurity researchers have revealed a new backdoor program able to stealing user login recommendations, device information and doing arbitrary commands on Cpanel systems.
The malware dropper has been dubbed “Facefish” simply by Qihoo 360 NETLAB staff owing its capabilities to supply several rootkits at different times and the use of Blowfish cipher to encrypt sales and marketing communications to the attacker-controlled server.
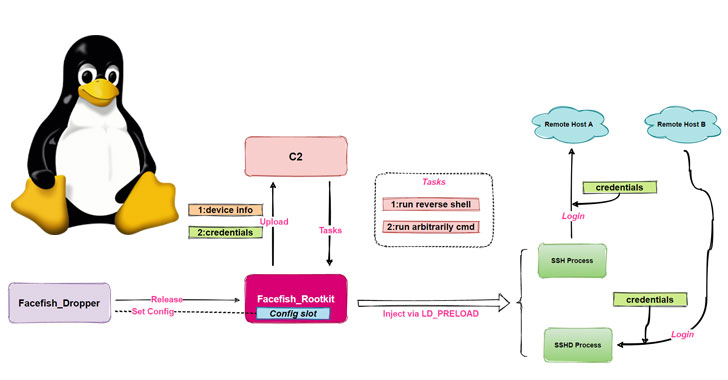
“Facefish consists of 2 parts, Dropper and Rootkit, and its major function is determined by the Rootkit module, which works with the Ring 3 layer and is crammed using the LD_PRELOAD feature of stealing user login credentials simply by hooking ssh/sshd program similar functions, and it also supports quite a few backdoor functions,” often the researchers said.
The NETLAB research builds on a former analysis published by Wacholder Networks on April dua puluh enam, which documented an attack sequence targeting Control Web Screen (CWP, formerly CentOS Net Panel) to inject a SSH implant with information exfiltration capabilities.
Facefish passes through a multi-stage infection approach, which commences with a demand injection against CWP to help retrieve a dropper (“sshins”) from a remote server, which in turn releases a rootkit the fact that ultimately takes charge connected with collecting and transmitting vulnerable information back to the hardware, in addition to awaiting further directions issued by the command-and-control (C2) server.
While the exact susceptability exploited by the attacker regarding initial compromise remains ambiguous, Juniper noted that CWP has been plagued by dozens connected with security issues, adding the “intentional encryption and obfuscation” of the source program code has made it “difficult to find out which versions of CWP are or remain at risk of this attack.”
For it has the part, the dropper is sold with its own set of tasks, primary among being detecting often the runtime environment, decrypting some sort of configuration file to get C2 information, configuring the rootkit, and starting the rootkit by injecting it into your secure shell server approach (sshd).
Rootkits are particularly harmful as they allow attackers to find elevated privileges in the program, allowing them to interfere with core businesses conducted by the underlying os. This ability of rootkits to camouflage into the textile of the operating system gives assailants a high level of stealth in addition to evasion.
Facefish also engages a complex communication protocol in addition to encryption algorithm, using directions starting with 0x2XX to exchange community keys and BlowFish regarding encrypting communication data together with the C2 hardware. Some of the C2 commands sent by the server are as follows –
- 0x300 – Report stolen credential information
- 0x301 – Collect details of “uname” command
- 0x302 – Run slow shell
- 0x310 – Execute just about any system command
- 0x311 – Mail the result of bash execution
- 0x312 – Report host information
NETLAB’s conclusions come from an analysis of the ELF sample file that detected in February 2021. Other indicators of endanger associated with the malware can be used here.
[ad_2]
Source link