[ad_1]
New upgrades have been made to a new Python-based “self-replicating, polymorphic bot” called Necro in exactly what is seen as an attempt to improve it is chances of infecting vulnerable techniques and evading detection.
“Although the bot was actually discovered earlier this year, the latest pastime shows numerous changes to the particular bot, ranging from different command-and-control (C2) communications and the add-on of new exploits for scattering, most notably vulnerabilities in VMWare vSphere, SCO OpenServer, Vesta Control Panel and SMB-based makes use of that were not present in the sooner iterations of the code,” researchers from Cisco Talos said in a deep-dive printed today.
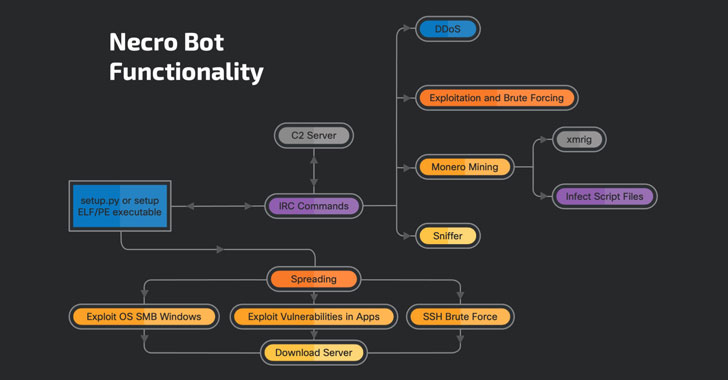
Said to be in enhancement as far back as 2015, Necro (aka N3Cr0m0rPh) targets both Cpanel and Windows devices, using heightened activity observed in the beginning of the year as part of malware viruses campaign dubbed “FreakOut” which was found exploiting vulnerabilities around network-attached storage (NAS) equipment running on Linux machines in order to co-opt the machines in a botnet for launching spread denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks together with mining Monero cryptocurrency.
In addition to its DDoS together with RAT-like functionalities to acquire and launch additional payloads, Necro is designed with caution in mind by installing a new rootkit that hides it is presence on the system. Even greater, the bot also drives malicious code to get back and execute a JavaScript-based miner from a remote server in HTML and PHP data on infected systems.
While previous versions of the spyware and adware exploited flaws in Liferay Portal, Laminas Project, together with TerraMaster, the latest variants witnessed on May 11 and 16 feature command injection makes use of targeting Vesta Control Panel, ZeroShell 3.9.0, SCO OpenServer 5.0.several, as well as a remote code setup flaw impacting VMWare vCenter (CVE-2021-21972) that was patched with the company in February.
A version of the botnet, unveiled on May 18, also includes makes use of for EternalBlue (CVE-2017-0144) together with EternalRomance (CVE-2017-0145), both of which will abuse a remote code setup vulnerability in Windows SMB protocol. These new upgrades serve to highlight that the spyware and adware author is actively establishing new methods of spreading by using advantage of publicly disclosed weaknesses.
Also of note could be the incorporation of a polymorphic engine in order to mutate its source passcode with every iteration while having the original algorithm intact inside a “rudimentary” attempt to limit the probability of being detected.
“Necro Python bot shows an acting professional that follows the latest development around remote command execution makes use of on various web purposes and includes the new makes use of into the bot,” Talos researchers said. “This raises its chances of spreading together with infecting systems. Users must make sure to regularly apply the newest security updates to all with the applications, not just operating systems.”
[ad_2]
Source link