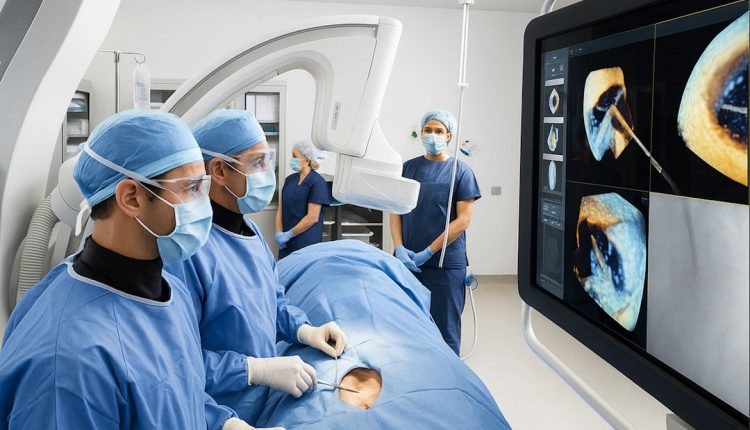
Healthcare systems around the world are under mounting pressure. Aging populations, chronic disease prevalence, workforce shortages, and financial constraints are straining hospitals to their limits. In response, artificial intelligence (AI) automation is emerging not as a futuristic concept, but as a practical and necessary component of modern healthcare infrastructure. From diagnostics and triage to administrative workflows and robotic surgery, AI is redefining how hospitals operate and how care is delivered.
TLDR: AI automation is rapidly transforming hospitals by improving diagnostic accuracy, optimizing workflows, and supporting clinical decision-making. It enhances efficiency, reduces administrative burden, and enables more personalized patient care. While challenges related to ethics, regulation, and data privacy remain, AI is poised to become a foundational element of hospital operations. The future of healthcare will likely be shaped by a careful balance between human expertise and intelligent automation.
The integration of AI into hospitals represents more than incremental technological progress. It signals a structural shift in healthcare delivery. Rather than replacing clinicians, AI systems are being developed to augment human judgment, reduce repetitive tasks, and increase the precision and speed of medical interventions. Hospitals that embrace this transformation are positioning themselves to deliver safer, more efficient, and more responsive care.
The Expanding Role of AI in Clinical Decision-Making
Table of Contents
One of the most impactful applications of AI in hospitals is in clinical decision support. Machine learning algorithms trained on vast datasets can identify patterns that may be difficult for humans to perceive. These systems assist physicians in making more accurate diagnoses, predicting disease progression, and selecting optimal treatment plans.
Image not found in postmetaAI-powered diagnostic tools are already being used in radiology, pathology, cardiology, and oncology. For example:
- Radiology: AI algorithms can detect subtle anomalies in X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, sometimes identifying early-stage disease before symptoms manifest.
- Pathology: Digital pathology systems use image recognition to analyze tissue samples with remarkable speed and consistency.
- Cardiology: Predictive models assess the risk of heart attacks or arrhythmias based on patient-specific variables.
- Oncology: AI assists in identifying genetic mutations and recommending personalized cancer therapies.
Importantly, these systems do not function in isolation. They operate as advisory tools, providing evidence-based insights that clinicians interpret within a broader clinical context. Studies increasingly show that when physicians collaborate with AI systems, diagnostic accuracy improves compared to either working alone.
Automation of Hospital Operations and Workflow
Beyond direct patient care, hospitals are complex organizations with extensive administrative and logistical demands. AI automation is playing a critical role in optimizing these operations, reducing inefficiencies that have historically burdened healthcare professionals.
Administrative tasks such as scheduling, billing, documentation, and insurance verification consume a significant portion of hospital resources. AI-powered automation systems can:
- Automate medical coding and claims processing.
- Reduce documentation time through intelligent voice recognition and natural language processing.
- Optimize staff scheduling based on patient flow predictions.
- Improve supply chain management by forecasting demand for medications and equipment.
In emergency departments, predictive analytics can anticipate patient surges by analyzing historical trends, seasonal data, and local health indicators. This enables proactive staffing adjustments and resource allocation, helping to reduce overcrowding and waiting times.
Hospital administrators are increasingly recognizing that AI-driven workflow optimization directly correlates with improved patient satisfaction and lower operational costs. By minimizing unnecessary delays and human error, automation enhances reliability and consistency across departments.
Robotics and AI-Assisted Procedures
Robotics integrated with AI is reshaping surgical and interventional procedures. While robotic-assisted surgery has been in use for years, the next generation of systems incorporates machine learning to improve precision and adapt in real time.
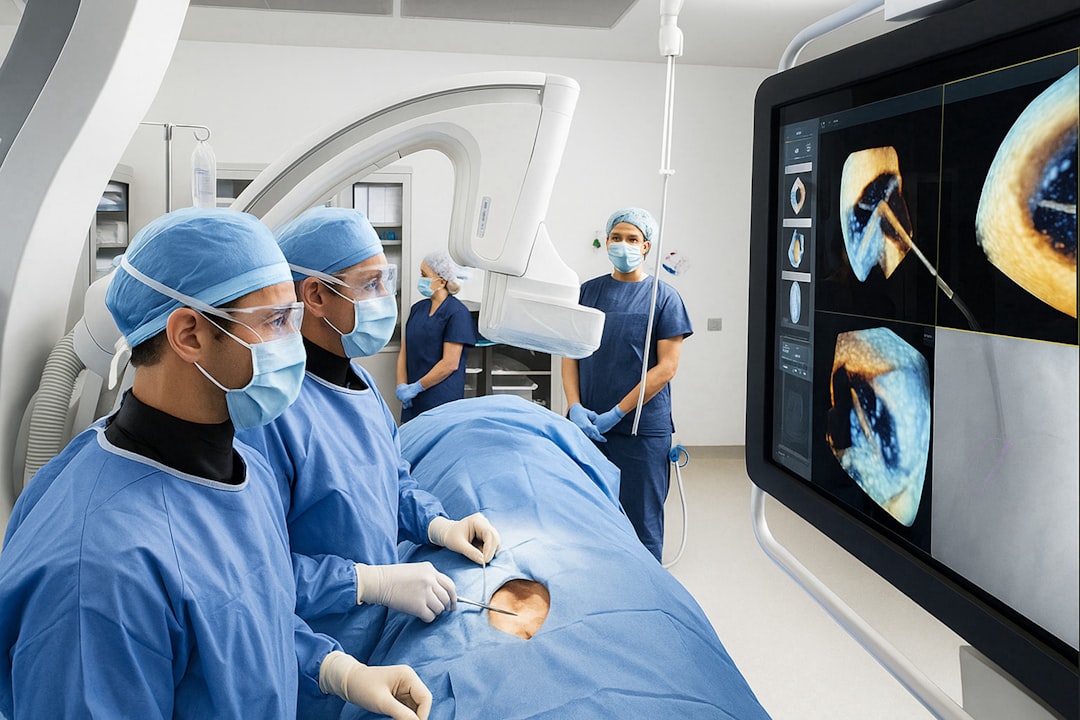
AI-enhanced surgical systems offer several advantages:
- Greater precision: Micro-movements are stabilized, reducing tremors and enhancing surgical accuracy.
- Data-driven insights: Surgical outcomes are continuously analyzed to refine techniques.
- Minimally invasive approaches: Smaller incisions often result in faster recovery and fewer complications.
- Remote capabilities: In some cases, expert surgeons can provide guidance or perform procedures from distant locations.
In addition to surgery, robotic automation is being deployed in pharmacies, laboratories, and patient transport. Automated medication dispensing systems reduce dosing errors, while robotic lab automation accelerates test processing times. These innovations free clinicians to focus on direct patient care rather than repetitive tasks.
Enhancing Patient Monitoring and Predictive Care
AI automation is also transforming patient monitoring within hospitals. Continuous data streams from wearable devices, bedside monitors, and electronic health records (EHRs) can be analyzed in real time to detect early signs of deterioration.
Predictive analytics models can:
- Identify patients at risk of sepsis hours before symptoms become critical.
- Detect early signs of respiratory failure.
- Reduce unexpected ICU transfers by flagging subtle warning patterns.
- Predict readmission risks to guide discharge planning.
These capabilities mark a shift from reactive to proactive care. Instead of responding to emergencies after they occur, clinicians can intervene earlier, often preventing complications entirely. This not only improves patient safety but also reduces the financial burden associated with extended hospital stays and critical care interventions.

For patients with chronic conditions, AI-powered systems can integrate hospital data with outpatient monitoring platforms. This creates a more seamless continuum of care, enabling hospitals to maintain oversight even after discharge.
Data Integration and Interoperability
One of the most challenging aspects of hospital modernization is integrating data across disparate systems. AI automation thrives on high-quality, interoperable data. As hospitals adopt standardized electronic records and cloud-based infrastructure, AI systems can analyze comprehensive patient histories rather than isolated data points.
Interoperability allows:
- Comprehensive patient profiles: Combining lab results, imaging, genetics, and clinical notes.
- Population health analytics: Identifying trends and risk factors across communities.
- Improved research capabilities: Leveraging anonymized datasets to accelerate medical discoveries.
With more cohesive data architectures, hospital systems gain a strategic advantage in both clinical and operational planning. However, this progress depends heavily on robust cybersecurity measures and strict compliance with data protection regulations.
Ethical Considerations and Human Oversight
Despite its promise, AI automation in hospitals raises legitimate concerns. Ethical use of AI requires transparency, accountability, and careful governance. Algorithms must be carefully validated to avoid bias, especially when trained on non-representative data.
Key considerations include:
- Data privacy: Protecting sensitive patient information against breaches.
- Algorithmic bias: Ensuring equitable care across demographics.
- Clinical accountability: Clarifying responsibility when AI-supported decisions impact outcomes.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting evolving national and international standards.
Hospitals must establish multidisciplinary oversight committees that include clinicians, data scientists, legal experts, and ethicists. AI systems should be continuously audited and updated to maintain safety and fairness. The goal is not to eliminate human judgment, but to strengthen it with technology that is transparent and rigorously validated.
The Workforce Implications of AI Automation
A common concern surrounding AI in hospitals is workforce displacement. In reality, most implementations are designed to augment rather than replace healthcare professionals. Administrative automation may reduce clerical workload, allowing nurses and physicians to devote more attention to patient interaction.
At the same time, new roles are emerging within hospitals, including:
- Clinical informatics specialists.
- AI system auditors and analysts.
- Data governance officers.
- Digital health integration managers.
Training and education will be essential. Medical curricula are beginning to incorporate data literacy and AI fundamentals, ensuring that future clinicians are equipped to work effectively alongside intelligent systems.
Looking Ahead: A Balanced Future
The future of healthcare will not be defined by machines replacing humans, but by a collaborative integration of advanced automation with clinical expertise. Hospitals that successfully adopt AI will likely experience:
- Higher diagnostic accuracy.
- Reduced operational inefficiencies.
- Improved patient outcomes and safety.
- More personalized and data-driven care pathways.
However, progress must be deliberate and responsibly managed. Investment in infrastructure, cybersecurity, regulatory alignment, and workforce training will determine how effectively hospitals leverage AI’s potential.
AI automation is no longer a speculative innovation. It is becoming a core pillar of hospital strategy and healthcare transformation. As technology continues to mature, the most successful healthcare institutions will be those that integrate AI not as a novelty, but as a disciplined, evidence-based extension of medical practice. In doing so, they will reshape the hospital experience—making it safer, more efficient, and better equipped to meet the complex demands of modern medicine.